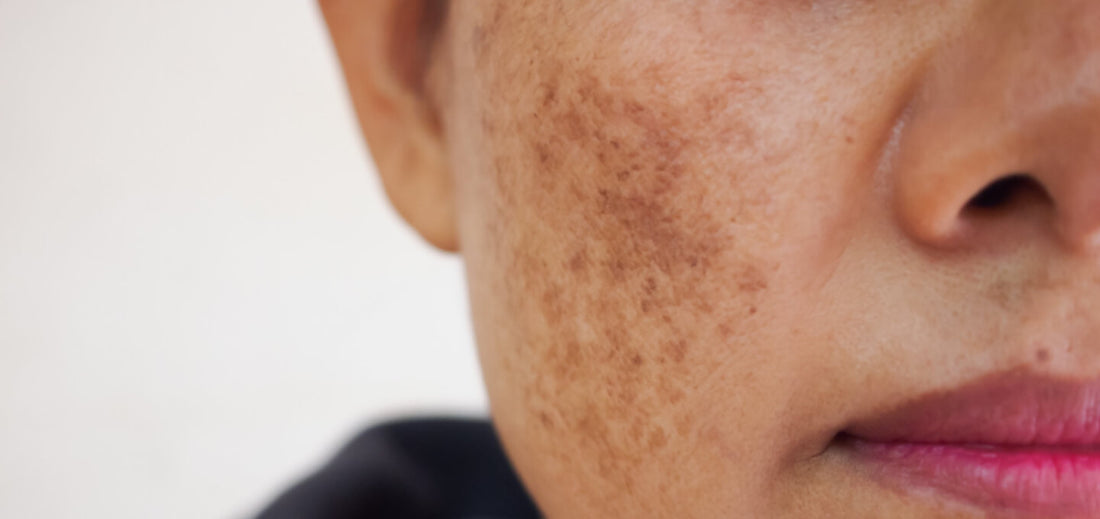
The Best Ways to Treat Melasma, According to Dermatologists
Melasma, often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy,” is a common skin condition that causes dark, discoloured patches to appear on the face. It typically affects areas such as the forehead, cheeks, upper lip, and chin, and is more common in women, especially during pregnancy or when using hormonal treatments like birth control. While melasma is not harmful or painful, it can be a source of self-consciousness for many.
If you’re struggling with melasma, you’re not alone. Thankfully, dermatologists have developed a variety of treatments to help manage and reduce the appearance of these stubborn spots. In this blog post, we’ll break down the best dermatologist-approved treatments for melasma, from topical creams to professional procedures.
What Causes Melasma?
Before we dive into the treatments, it's important to understand what causes melasma. This condition is largely triggered by overactive pigment-producing cells in the skin, known as melanocytes. Factors such as hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy, birth control, hormone replacement therapy), sun exposure, and genetics can stimulate these cells, leading to hyperpigmentation.
Sun exposure is a key trigger for melasma, as ultraviolet (UV) rays stimulate melanocytes to produce more pigment. For this reason, melasma is more noticeable during the summer months or after sun exposure, and it’s often exacerbated by pregnancy or the use of birth control pills.
The Best Treatments for Melasma
While melasma can be stubborn and difficult to treat, there are several options that dermatologists recommend to lighten and fade the dark spots. Depending on the severity and your skin type, you may need a combination of treatments to achieve the best results.
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are the first line of defence against melasma. Dermatologists often recommend a combination of products that can help lighten the skin and inhibit the production of melanin (the pigment responsible for dark spots).
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is considered one of the most effective treatments for melasma. This skin-lightening agent works by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in the production of melanin. It can help reduce the appearance of dark patches over time.
- How it works: Hydroquinone blocks melanin production, lightening the dark spots and evening out skin tone.
- Use: It’s typically available in both over-the-counter and prescription strengths. Your dermatologist will recommend the appropriate concentration based on your skin’s needs.
Tip: While hydroquinone is effective, it can cause irritation or sensitivity in some people, so it’s important to use it under the guidance of a dermatologist.
Retinoids (Retinol and Tretinoin)
Retinoids are derived from vitamin A and work by speeding up cell turnover, which helps to shed dead skin cells and fade dark spots. Retinoids can also improve skin texture, helping to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, which may be beneficial for those with melasma and ageing skin.
- How it works: Retinoids stimulate the production of new skin cells, helping to fade hyperpigmented areas and improve overall skin tone.
- Use: Prescription-strength tretinoin is often used for melasma, but milder over-the-counter retinols can also be effective for less severe cases.
Tip: Retinoids can increase skin sensitivity, so it’s essential to use sunscreen daily when using these products, and avoid applying them if you’re pregnant or breastfeeding unless approved by your doctor.
Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid is another skin-lightening ingredient that works well for treating melasma. It has both exfoliating and anti-inflammatory properties, making it an excellent choice for sensitive skin types.
- How it works: Azelaic acid helps inhibit melanin production and also promotes the shedding of pigmented skin cells.
- Use: It’s available in both prescription and over-the-counter formulations, with concentrations typically ranging from 10% to 20%.
Tip: Azelaic acid is generally well-tolerated by most skin types, including sensitive skin, and may be a gentler option than hydroquinone or retinoids.
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant known for its skin-brightening properties. It helps lighten hyperpigmented areas by inhibiting melanin production and can also protect against further damage from UV rays.
- How it works: Vitamin C works as an antioxidant, neutralising free radicals and helping to prevent further pigmentation. It also helps to break up existing pigment in the skin.
- Use: Vitamin C is available in many serums and creams and is typically used in the morning before applying sunscreen.
Tip: For best results, use a stable form of Vitamin C, such as ascorbic acid, and ensure it’s in an airtight container to prevent oxidation.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the top layers and helps to remove dark pigmented cells. Chemical peels are often used in more persistent or severe cases of melasma when topical treatments alone aren’t sufficient.
- How it works: The peel removes the outer layer of the skin, allowing fresh, new skin to emerge. This process can lighten hyperpigmentation and improve skin tone.
- Types of peels: Dermatologists often use glycolic acid, salicylic acid, or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peels for melasma, depending on the severity of the pigmentation and skin type.
Tip: Chemical peels should only be performed by a licensed dermatologist, as incorrect use can lead to irritation or worsening of pigmentation. Multiple treatments may be needed for the best results.
3. Laser Treatments
Laser therapy is an advanced treatment option for melasma that can target and break up pigment deep within the skin. Laser treatments are often used for cases that don’t respond to topical treatments alone.
Fractional CO2 Laser
This laser is designed to target deeper layers of the skin, stimulating collagen production and addressing both the melasma and overall skin texture.
- How it works: The fractional CO2 laser targets melanin in the skin, breaking up the pigment to reduce the appearance of dark spots.
- Use: It is often recommended for deeper, more resistant cases of melasma.
Tip: Laser treatments can be effective, but they carry the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin types. Be sure to consult with a dermatologist experienced in treating melasma with lasers.
Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser
The Q-switched Nd:YAG laser is a non-ablative treatment that targets pigment without damaging the surrounding skin. This laser is often recommended for superficial pigmentation.
- How it works: It targets the pigment directly, breaking it down into smaller particles that are eventually removed by the skin’s natural healing process.
- Use: It’s a popular treatment for those with sensitive skin or those prone to scarring.
Tip: Like with chemical peels, laser treatments should only be performed by experienced dermatologists to ensure safe and effective results.
4. Sun Protection: The Most Important Step
Regardless of which treatments you choose, sun protection is crucial when managing melasma. Exposure to UV rays can worsen existing pigmentation and cause new spots to form.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 every day, even on cloudy days or indoors near windows.
- Apply sunscreen generously to all exposed areas of the skin, and reapply every two hours if you're outside.
- Consider wearing a wide-brimmed hat and protective clothing to shield your skin from direct sun exposure.
Tip: Look for sunscreens with added antioxidants (such as Vitamin C) to provide extra protection against environmental damage.
Final Thoughts
Melasma is a challenging condition, but with the right approach, it can be managed effectively. Dermatologists typically recommend a combination of topical treatments, professional procedures, and daily sun protection to achieve the best results. Whether you choose hydroquinone, retinoids, chemical peels, or laser treatments, a tailored plan that suits your skin type and the severity of your melasma will give you the best chance of success.
As always, consult with a qualified dermatologist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your unique needs. With the right care and consistency, melasma doesn’t have to hold you back from glowing, healthy skin.